Finding the most similar questions on r/AskReddit
Introduction
In r/AskReddit, users can submit open-ended questions to which other users can then reply with answers. The subreddit describes its focus as “to ask and answer questions that elicit thought-provoking discussions”. It has been one of the most popular subreddits on Reddit.
In this post, I will analyze the top 1,000 questions from r/askreddit and threads that are most similar to each other. This technique can be used for a few purposes:
- Recommend similar questions to the one that a user is reading in order to increase user engagement
- Identify reposted questions, which is undesirable user experience for readers
- Outside of forums, this can also be used in news site. Publishers can show relevant news pieces about a particular topic that the user is reading
 Top posts of the year
Top posts of the year
Methodology
I fetched 1,000 highest rated questions in the month. These rankings are based on users upvotes.
Step-by-step data processing
- Remove english stop words. Common words such as ‘the’, ‘and’, ‘I’ appear frequently but by themselves don’t convey insight into the topic of the question. We want to remove them so that they won’t inflate our similarity scores.
- Stem words using nltk (removing plurals, stemming verbs in different tenses, etc).
- Convert raw text string to vector using bag-of-word method, using term frequency - inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) method.
- Use cosine similarity metric to find the closest matching thread name.
- Similarity score ranges from 0 to 1 with 1 being an exact match.
- Note that due to our preprocessing above, questions that are originally slightly different may still have a score of 1
- The dimension of the output is a 1,000 x 1,000 dataframe where each row and each column represent a question. For each row, our goal is to find the column index containing the highest score. Note that, in the main diagonal, values will always be 1 because it’s the row and column are representing the same question. To prevent this, we will set the main diagonal of the matrix to 0 using
np.fill_diagonal
Results and Observations
- Thread names are usually short. Therefore using raw word count will yield higher similarity score than tf-idf because of common phrases that are not filted as stop words (eg. what, you(r), etc.)
- tf-idf works slightly better because rarer topics can be matched
| original thread name | best match | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | What would you do if you woke up in the 80’s? | What’s your favorite 80’s movie? |
| 1 | What is your strange turn-on? | what’s the weirdest thing that’s turned you on? |
| 2 | What’s worse than a wet handshake? | What is 100% worse when wet? |
| 3 | Zoo workers of reddit, what is the dumbest thing someone has asked about an animal? | What’s the dumbest thing you believed as a child? |
| 4 | What is your favorite bromance in fiction? | Who is your favorite fictional doctor? |
| 5 | Women of reddit, whats the stupidest excuse a man has ever given you to not wear a condom? | Women of reddit, what is the grossest thing a man has said to you? |
| 6 | The world is now under the iron fist of Canada. What changes? | What is the most disturbing fact you know about Canada? |
| 7 | what’s a song that everybody knows? | What do you hate that everybody seems to love? |
| 8 | When it comes to dating apps, what is an automatic “pass” for you? | WWhat must one never do on a first date? |
| 9 | Who’s someone you looked up to or idolized as a kid that you now can’t stand? | Who is a famous singer that you cannot stand their singing voice? |
Takeaways
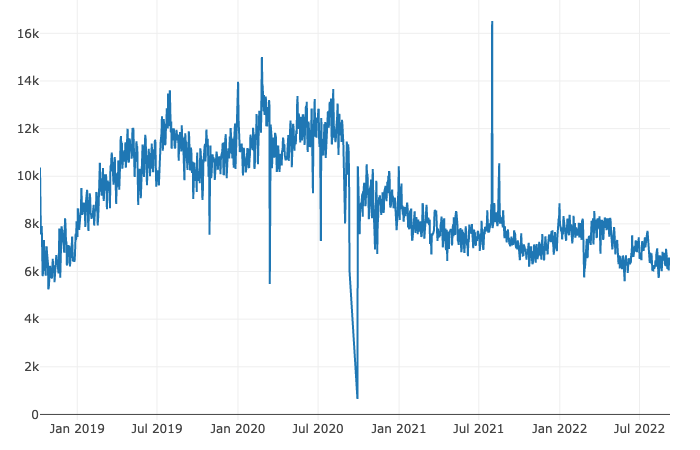 Number of daily posts on r/AskReddit, retrieved on 10 Sep 2022. Source: subredditstats.com
Number of daily posts on r/AskReddit, retrieved on 10 Sep 2022. Source: subredditstats.com
- In this post I only compared data from a group of 1,000 posts, which is not a big number compared to the averaged more than 6,000 posts per day. This is a limit from PRAW. I can potentially look for alternative sources that archive reddit posts and do an offline analysis (for exammple: monthly data). With more data points, the matching process will most likely improve.
- Some of the matches found are not strictly accurate (potentially due to lacking of similar questions), but interesting. As a owner, I think this algo strike a good balance between producing good enough results and being simple to implement.
The full code
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
from nltk.stem.snowball import SnowballStemmer
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 500)
np.random.seed(9) # to fix sampled data
orig_corpus = []
with open('data/1000posts.txt') as file:
for line in file:
orig_corpus.append(line.replace('\n', ''))
stemmer = SnowballStemmer('english')
def stem_tokens(text):
text = text.strip()
words = text.lower().split()
words = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in words]
return ' '.join(words)
corpus = [stem_tokens(_) for _ in orig_corpus]
# thread1: orignal list of thread name
# sim-tf: closest match, using term frequency
# sim-tf-idf: closest mathh, using term frequency - inverse document frequency
df = pd.DataFrame({
'orig_thread': orig_corpus,
'stemmed_thread': corpus})
df.head()
# using raw count
count_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(stop_words='english', min_df=0.005)
X_count = count_vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
# most frequent words
word_freq = pd.DataFrame({
'word': count_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out(),
'freq': X_count.toarray().sum(axis=0)
})
word_freq_15 = word_freq.sort_values(by='freq', ascending=False).head(15)
# plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 3))
ax.bar(
x=word_freq_15['word'].values,
height=word_freq_15['freq'].values,
width=1,
ec='white'
)
ax.set_title('Top 15 words by count')
fig.savefig('./assets/top_15.png', bbox_inches='tight')
df_count = pd.DataFrame(X_count.toarray(), columns=count_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out())
df_count_sim = pd.DataFrame(cosine_similarity(df_count, dense_output=True))
df_count_sim_as_np = df_count_sim.values
np.fill_diagonal(df_count_sim_as_np, 0)
df_count_result = pd.DataFrame(df_count_sim_as_np)
df_count_result['best_match (count)'] = df_count_result.idxmax()
df_count_result['similarity (count)'] = df_count_result.max()
count_result = df_count_result[['best_match (count)', 'similarity (count)']]
df = df.merge(count_result, how='left', left_index=True, right_index=True)
# using tf-idf
tfidf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words='english')
X_tfidf = tfidf_vectorizer.fit_transform(corpus)
df_tfidf = pd.DataFrame(X_tfidf.toarray(), columns=tfidf_vectorizer.get_feature_names_out())
df_tfidf_sim = pd.DataFrame(cosine_similarity(df_tfidf, dense_output=True))
df_tfidf_sim_as_np = df_tfidf_sim.values
np.fill_diagonal(df_tfidf_sim_as_np, 0)
df_tfidf_result = pd.DataFrame(df_tfidf_sim_as_np)
df_tfidf_result['best_match (tf-idf)'] = df_tfidf_result.idxmax()
df_tfidf_result['similarity (tf-idf)'] = df_tfidf_result.max()
tfidf_result = df_tfidf_result[['best_match (tf-idf)', 'similarity (tf-idf)']]
df = df.merge(tfidf_result, how='left', left_index=True, right_index=True)
df['best_match (count)'] = df['best_match (count)'].map(df['orig_thread'].to_dict())
df['best_match (tf-idf)'] = df['best_match (tf-idf)'].map(df['orig_thread'].to_dict())
# compare
# random 10
sample_index = np.random.randint(0, len(corpus), 10)
print(df.loc[sample_index][['orig_thread', 'best_match (count)', 'best_match (tf-idf)']].reset_index().to_markdown())
# plot
bins = [_/10 for _ in range(0, 11)]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.clear()
pd.cut(tfidf_result['similarity'], bins=bins).value_counts().sort_index().plot(ax=ax, kind='bar', width=1, ec='white', alpha=.3, color='#fb553b', label='tf-idf')
pd.cut(count_result['similarity'], bins=bins).value_counts().sort_index().plot(ax=ax, kind='bar', width=1, ec='white', alpha=.3, label='raw count')
ax.legend(loc='upper center', bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, 1.05), ncol=2)
fig.savefig('./assets/compare sim score.png', bbox_inches='tight')